Inline View SQL
Inline SQL View
Inline View is SQL script with programmatic logic inside, so that you can build dynamic SQL for reports control from parameter. With this feature you can apply various and complex business scenarios into SQL.
The SQL executed finally generated is inline SQL which is sub query with joined with other table or other Inline View also.
Creating SQL Inline View
|
Create new SQL Inline View |
|
|
|
|
|
1 |
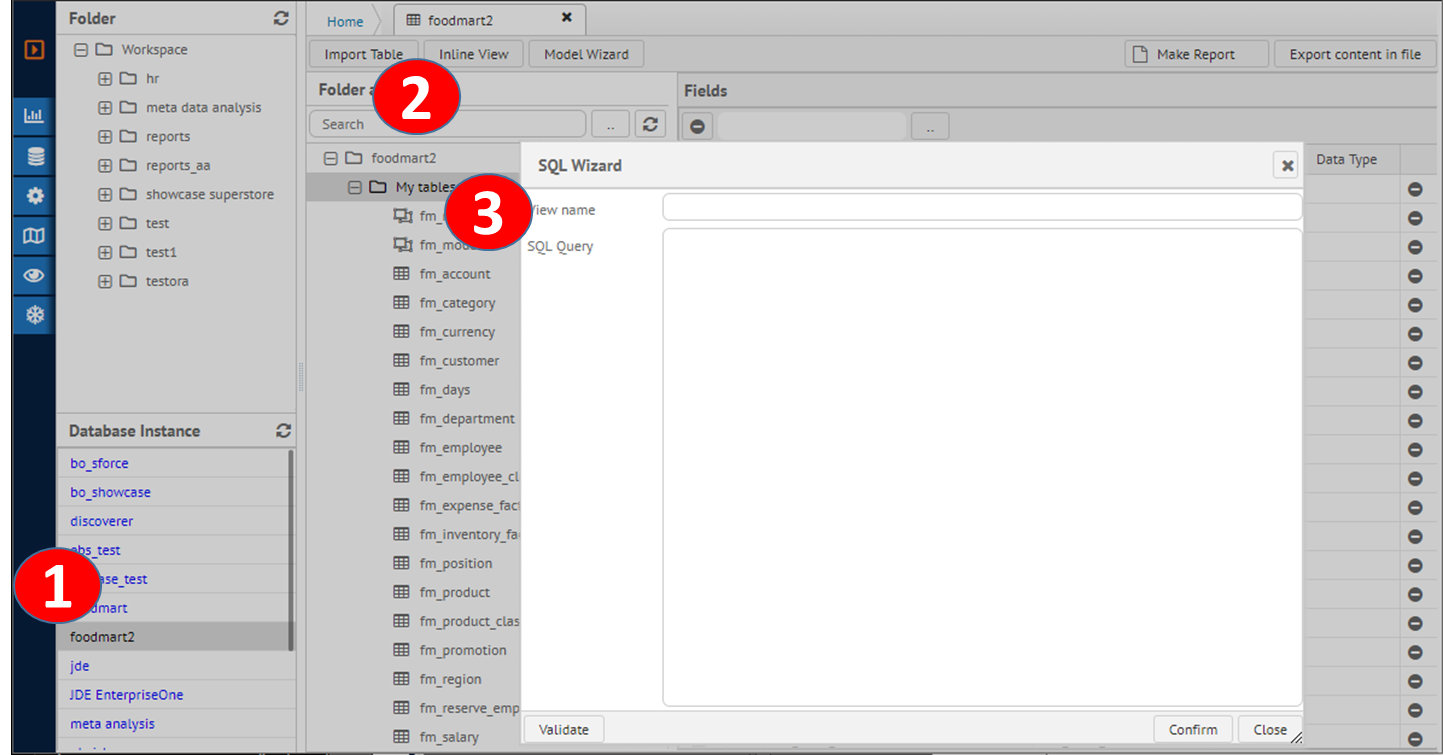
Click on database instance to work with analysis. |
|
2 |
Click on Inline View button to register new InlineView query. |
|
3 |
On the SQL Wizard type your SQL and dynamic operator on the text area. |
|
4 |
Click on confirm button to save contents. |
Editing SQL
Click on Inline view and click on Edit button next to item name.
Advanced Tag for InlineView SQL
SQL + Programming logic is fundamental requirements to make your application more flexible and adaptive with various business scenarios. You can implement conditional operation, and precalcuation of parameters, and parameter checking with advanced tags.
InlineView is part of subquery inside of main query. On the cubemodel, you can make join between InlineView / Table or InlineView/InlineView. The final SQL query is generated with subquery on the following format.
For the InlineView syntax, *SELECT * FROM FM_CUSTOMER*. The report AdHoc query generator generates query with *SELECT * FROM (SELECT * FROM FM_CUSTOMER) n10, FM_PRODUCTS n20 INNER JOIN n10.PRODUCT_ID=n20.PRODUCT_ID*
Dynamic Query
Dynamic Query includes Conditional processing of SQL. Using IF / ELSE / END IF you can make programmatic implementation for your SQL view objects. And also parameters with filter values, and preprocessing is ultimate solution for adopting various business scenarios and make flexible for your analysis query.
Example Dynamic Query
|
#set cur_month=${cur_month} ? ${cur_month} : "200501" |
SQL Query Parts
Preprocessors
On this preprocessor line, you can put calculation or formulas to be calculated using parameters and assign value to parameters.
SQL Query
The main parts of SQL query which includes SELECT, FROM and tables.
We recommend to use fields with alias name to make proper name on SQL.
|
-- NOT RECOMMENDED
|
Conditional Operations
Example of Conditional Operation
|
#set lparam = helper.systemDate("yyyyMMdd")
|
Helper Functions
Bellow is Helper functions predefined on package.
|
Function |
Input |
Output |
Description |
|
systemDate |
String dateFormat |
String |
Current server time |
|
getDate |
String datevalue |
String |
Input date |
About Preprocessor
Preprocessor Starts with # symbol, and placed anywhere in SQL query. The line starts with # is assumed that preprocessor line. On this preprocessor line, you can put calculation or formulas to be calculated using parameters and assign value to parameters.
Preprocessor Syntax
|
Operator |
Description |
Notes |
|
Boolean and |
The usual && operator can be used as well as the word and, e.g. |
|
|
Boolean or |
The usual || operator can be used as well as the word or, e.g. |
|
|
Boolean not |
The usual ! operator can be used as well as the word not, e.g. |
|
|
Bitwise and |
The usual | operator is used, e.g. |
|
|
Bitwise xor |
The usual ^ operator is used, e.g. |
|
|
Bitwise complement |
The usual ~ operator is used, e.g. |
|
|
Ternary conditional ?: |
The usual ternary conditional operator condition ? if_true : if_false operator can be used as well as the abbreviation value ?: if_false which returns the value if its evaluation is defined, non-null and non-false, e.g. |
|
|
Equality |
The usual == operator can be used as well as the abbreviation eq. For example |
|
|
Inequality |
The usual != operator can be used as well as the abbreviation ne. For example |
|
|
Less Than |
The usual < operator can be used as well as the abbreviation lt. For example |
|
|
Less Than Or Equal To |
The usual <= operator can be used as well as the abbreviation le. For example |
|
|
Greater Than |
The usual > operator can be used as well as the abbreviation gt. For example |
|
|
Greater Than Or Equal To |
The usual >= operator can be used as well as the abbreviation ge. For example |
|
|
In or Match=~ |
The syntactically Perl inspired =~ operator can be used to check that a string matches a regular expression (expressed either a Java String or a java.util.regex.Pattern). For example "abcdef" =~ "abc.* returns true. It also checks whether any collection, set or map (on keys) contains a value or not; in that case, it behaves as an "in" operator. Note that it also applies to arrays as well as "duck-typed" collection, ie classes exposing a "contains" method. "a" =~ ["a","b","c","d","e",f"] returns true. |
|
|
Not-In or Not-Match!~ |
The syntactically Perl inspired !~ operator can be used to check that a string does not match a regular expression (expressed either a Java String or a java.util.regex.Pattern). For example "abcdef" !~ "abc.* returns false. It also checks whether any collection, set or map (on keys) does not contain a value; in that case, it behaves as "not in" operator. Note that it also applies to arrays as well as "duck-typed" collection, ie classes exposing a "contains" method. "a" !~ ["a","b","c","d","e",f"] returns true. |
|
|
Addition |
The usual + operator is used. For example |
|
|
Subtraction |
The usual - operator is used. For example <pre> val1 - val2 </pre> | |- |Multiplication |<nowiki>The usual / operator is used, or one can use the div operator. For example |
|
|
Modulus (or remainder) |
The % operator is used. An alternative is the mod operator. For example |
|
|
Negation |
The unary - operator is used. For example<nowiki> <pre> -12 </pre> | |- |Array access |<nowiki>Array elements may be accessed using either square brackets or a dotted numeral, e.g. |
|
|
HashMap access |
Map elements are accessed using square brackets, e.g. |